How to start Business in Saudi - Full Checklist
Saudi Arabia, the heart of the Middle East, has emerged as a thriving hub for businesses and investors. With its rich resources, strategic location, and progressive policies, the Kingdom offers a fertile ground for various industries to flourish.
The Saudi government has taken substantial steps to foster a business-friendly environment, leading to booming investment opportunities. From tech startups to large-scale manufacturing, the doors are wide open for innovators and entrepreneurs.
Central to this transformation is the regulatory framework that governs business operations within the country. Comprised of a series of laws and regulations, it serves to protect both businesses and consumers. The Ministry of Commerce (MOC), plays a pivotal role in this landscape, acting as the gateway for commercial registration and ensuring adherence to the country's trade laws.
Investing in Saudi Arabia is not just about tapping into a market; it's about becoming part of a growing economic ecosystem that encourages creativity, innovation, and collaboration.
To run a successful business in Saudi you need accounting software that you can trust with your financial management, Use Wafeq and focus more on growing your business.
To run a successful business in Saudi you need accounting software that you can trust with your financial management, Use Wafeq and focus more on growing your business.
Selecting Industry, Business Structure, and Trade Name
The first step in starting a business in Saudi Arabia is selecting the right industry, business structure, and trade name. This foundation will guide every decision thereafter.
Online Business Growth in Saudi Arabia
With 19.28 million online shoppers last year, the growth of e-commerce has been remarkable. The government has facilitated this transition through:
Platform Purpose
Importance of Industry Selection and Understanding Market Dynamics:
Choosing the right industry is crucial for success in the Saudi market. Understanding the market dynamics, demand, competition, and regulations specific to the industry enables an entrepreneur to make informed decisions and build a sustainable business. Market research, analysis of competitors, and alignment with the country's Vision 2030 are vital aspects of this stage.
Explanation of Different Business Structures:
Saudi Arabia offers a wide range of business structures catering to different needs and investment levels. Some of the common structures include:
- Sole Proprietorship: Owned by a single individual, offering complete control but also full liability.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): Provides limited liability to owners and generally requires at least two shareholders.
- Joint Stock Company: Suitable for larger investments, with shareholders' liability limited to their share in the capital.
- Partnerships: Various forms of partnerships exist, allowing flexibility in ownership and responsibility.
Saudi Arabia Business License
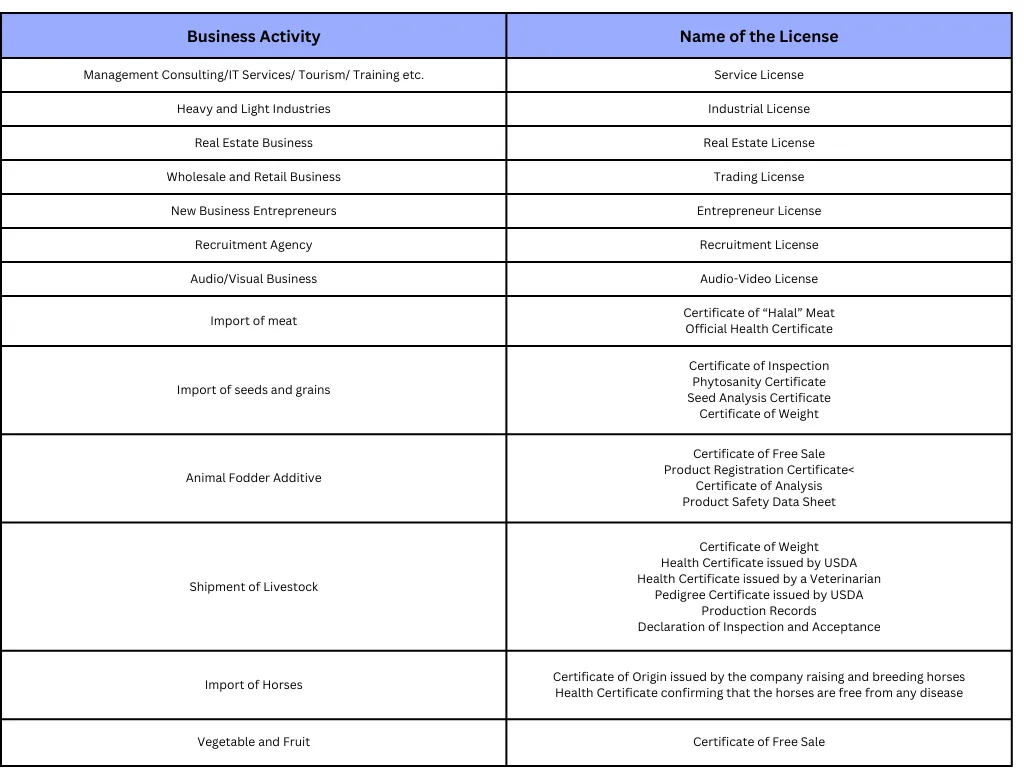
Read also: The best accounting software in Saudi Arabia.
Trade Name Selection:
Choosing a trade name is more than just a creative exercise; it represents the face of the business. The name must be unique, culturally respectful, and in accordance with the regulations set by the Ministry of Commerce (MOC). Limited companies must include "Limited" or "Ltd." in their names.
Each of these decisions plays a vital role in the overall success and sustainability of the business. Seeking professional guidance and thorough planning will streamline the process and contribute to long-term success.
Choosing and Registering a Trade Name; Legal Considerations
Choosing the right trade name is an integral part of establishing a business in Saudi Arabia. The trade name represents the brand's identity, so it must be selected with care. Here's what you need to know:
- Uniqueness: The trade name must not be a copy of existing competitors.
- Cultural Sensitivity: It must not sound offensive or contradict religious values.
- Legal Requirements: Limited companies must include "Limited" or "Ltd." in their name.
- Registration with the Ministry of Commerce (MOC): A trade name must be registered with the MOC to ensure compliance with all legal considerations.
Understanding Saudi Arabia's Corporate Rules
Starting a business in Saudi Arabia requires adherence to specific corporate rules and regulations. Here's an overview:
Overview of Essential Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
- Labor laws
- Taxation (including Zakat and Income Tax)
- Intellectual property laws
- Banking regulations
- Sector-specific regulations (e.g., healthcare, tourism)
Importance of Professional Advice on Local Regulations: Engaging a local expert who understands the specific legal landscape is crucial. Professional advice ensures that the business complies with all local laws, reducing the risk of legal complications down the line.
Business Planning and Document Submission
Successfully starting a business in Saudi Arabia requires careful planning and adherence to the specific document submission guidelines. Here's a detailed breakdown of the process:
Crafting a Business Plan and Its Importance:
Purpose: Defines the direction, objectives, and strategies of the business.
Components: Includes market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and operational plans.
Benefits: Enhances the probability of success, aids in obtaining financing, and helps in guiding the business through various stages.
List of Essential Documents for Registration:
- A duly filled company registration application form.
- A board resolution of the parent company approving the incorporation of the KSA entity.
- Copy of trade name confirmation.
- Identity and address proofs of business directors and shareholders.
- Memorandum of association (MOA) and Articles of association (AOA).
- Blueprint of the business, bank account reference letter, Power of attorney, etc.
- Third-party approvals (if any).
Arabic Translation Requirements:
All official documents must be translated into Arabic.
Certified professionals or entities must carry out translations.
Ensuring accurate translation is crucial for legal compliance and a smooth registration process.
Obtaining Necessary Approvals
Starting a business in Saudi Arabia necessitates gaining approvals from various government bodies, and understanding the specific requirements for different industries. Below is a closer look at this process:
A Detailed Look at the Approval Process from Various Governmental Bodies:
Ministry of Commerce (MOC): Company registration and trade name confirmation.
Chamber of Commerce: Membership and accreditation.
Labour Office, Municipality, GOSI, ZATCA: Various operational and legal approvals.
Respective Ministries for Specific Industries: E.g., Ministry of Health for the healthcare sector; Ministry of Tourism for tourism businesses.
Explaining the Specific Requirements for Different Industries:
Healthcare: Compliance with medical regulations, certifications, and staffing.
Tourism: Licensing, adherence to tourism guidelines, and collaboration with local tourism bodies.
Others: Requirements vary based on the nature of the industry, location, and type of services provided.
Overview of Physical Office Requirements:
Location Selection: Strategic location to target the market and adhere to local zoning laws.
Facility Requirements: Compliance with local building codes, safety standards, and accessibility.
Legal Approvals: Necessary permissions, inspections, and documentation as per Saudi Arabian regulations.
Read more: What is e-invoicing in Saudi Arabia?
Cost of Setting Up a Business in Saudi Arabia
Embarking on a business venture in Saudi Arabia requires an understanding of both the initial investment and ongoing operational expenses. Here's a comprehensive breakdown of the costs:
- Initial Investment:
Investment License at the General Investment Authority: A crucial step to gain legal clearance to operate, with fees varying based on the nature and scale of the business.
Legalization/Notarization of Documents: All official documents must be legalized and notarized, a process that incurs additional fees.
Publication in Official Gazette: Public announcement in the official gazette comes with a specific charge.
- Ongoing Expenses:
Office Establishment: Renting or buying office space, furnishing, utilities, and other facility-related expenses.
Banking: Opening a corporate bank account may involve charges, including account maintenance fees.
Chamber of Commerce Membership: Annual fees for maintaining the membership.
- Other Costs:
Licensing: Industry-specific licenses and permits, costs vary by sector.
Taxes: Compliance with the Saudi Arabian tax system, including income tax at corporate rates and individual rates.
- Additional Considerations:
Professional Services: Consultation with legal and business experts may be required.
Market Analysis and Business Planning: Costs related to research, planning, and strategizing.
By having a clear understanding of these costs, potential investors can prepare a well-structured financial plan that aligns with Saudi Arabian regulations and industry standards.
Taxation and Financial Considerations in Saudi Arabia
Overview of the Zakat and Tax Law:
Corporate Taxes: Saudi Arabia's taxation system operates under the Zakat and Tax Law enacted in 2018. Corporations are subjected to a 20% tax rate on income, profits, and capital gains.
Individual Taxes: Individuals are taxed progressively, with rates ranging from 2% to 45%, depending on the income level.
Financial Reporting and Auditing:
Accounting Standards: The accounting standards in Saudi Arabia adhere to the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Financial Records: Businesses must keep accurate financial records and prepare financial statements.
Auditing: Financial statements must be audited by a certified public accountant (CPA), ensuring compliance with regulations and transparency in financial dealings.
Banking and Investment Opportunities:
Banking: Businesses can open bank accounts with any commercial bank in the country, and they should be aware of potential account fees and requirements.
Investment Opportunities: The Saudi Arabian market offers a multitude of investment options, including stocks, real estate, and private equity. Collaborating with financial experts can lead to tailored investment strategies that suit the business's needs and risk profile.
Understanding and complying with these financial considerations are vital for the successful establishment and operation of a business in Saudi Arabia. Investors must be keenly aware of the taxation laws, financial reporting requirements, and available banking and investment options.
Read more: Income Tax, Zakat, And Other Taxes Simply Explained.
Intellectual Property Considerations in Saudi Arabia
Understanding Intellectual Property Rights:
Intellectual property (IP) laws play a crucial role in safeguarding innovation and creativity within businesses. Saudi Arabia's legal framework has strong provisions to protect the intellectual property rights of businesses and individuals. The main types of intellectual property that are protected under Saudi law include:
Copyrights: These protect original works of authorship, including literary works, music, and art. Saudi Arabia is a member of the Berne Convention, providing international protection for copyrighted works.
Trademarks: Trademarks safeguard symbols, names, and slogans used to identify goods and services. They help in building brand recognition and trust among consumers. The Saudi Trademark Law conforms to international standards, and trademarks can be registered with the Ministry of Commerce (MOC).
Patents: Patents protect inventions or discoveries, granting the inventor exclusive rights to use, make, or sell the invention for a certain period. The Saudi Patent Office, under the King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST), handles patent registration and enforcement.
Due Diligence Types in Saudi Arabia
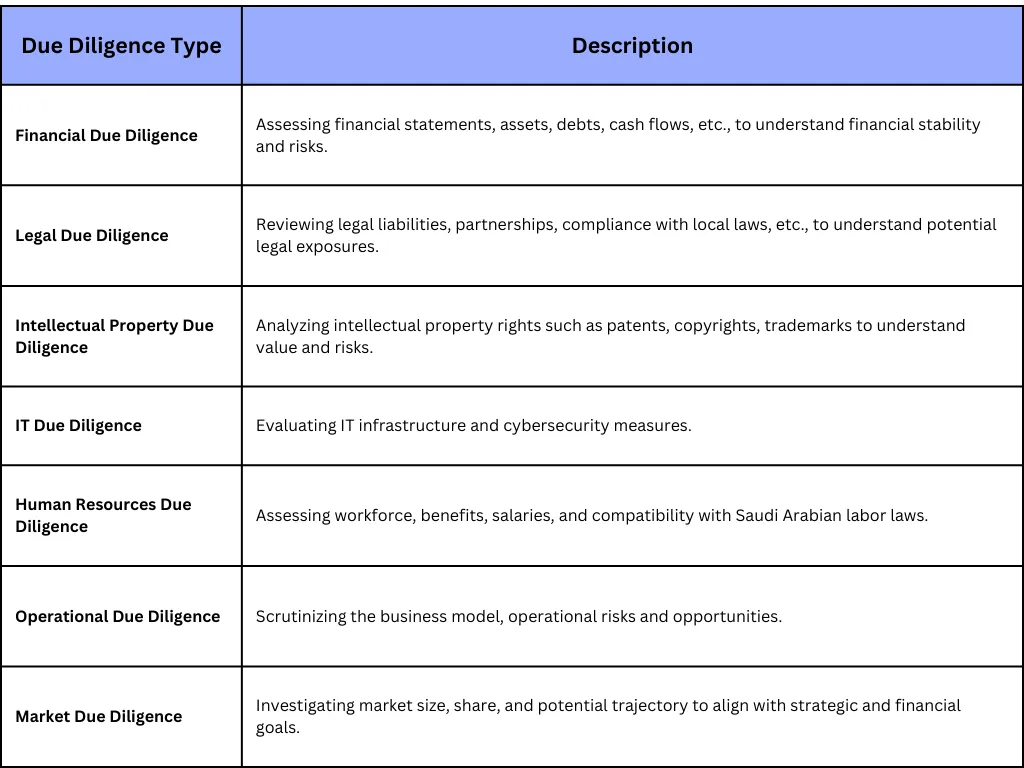
Conclusion
Starting a business in Saudi Arabia is an exciting and promising venture that combines a flourishing investment landscape with a clear and well-defined legal and regulatory framework. The process involves meticulous planning and adherence to guidelines such as selecting the industry, understanding local corporate rules, complying with legal requirements, obtaining necessary approvals, considering financial aspects including taxation, respecting intellectual property rights, and conducting thorough due diligence.
With a booming market and significant opportunities across various sectors, Saudi Arabia offers a conducive environment for investors. The support from the Ministry of Commerce and various governmental bodies, coupled with internationally recognized accounting standards and banking facilities, makes the process accessible and appealing. The comprehensive guidelines provided in this article act as a roadmap for aspiring business owners, emphasizing the importance of each step to ensure a successful establishment. By adhering to these principles, investors can confidently venture into Saudi Arabia's vibrant market, leveraging the nation's growth and potential.
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.


.png?alt=media)










