Financial Management: A Comprehensive Guide for Accountants and Business Owners

Financial Management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling an organization's or individual's financial resources. This process is the cornerstone for achieving monetary stability and success in the business realm. As a vital part of organizational operations, financial management seeks to ensure the efficient and effective use of resources by identifying financial goals and developing strategies to achieve them.
This article will guide accountants and business owners through the concept of financial management and its various aspects, enabling them to enhance the financial performance of their businesses.
The Importance of Financial Management:
"Financial management is crucial in achieving sustainability and growth in any business endeavor. It helps define financial goals and priorities and ensures that financial resources are used efficiently. It also aids in reducing financial risks and increasing the ability to generate profits. For accountants and business owners, understanding the importance of financial management is a fundamental step toward achieving lasting success.
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.
Principles of Financial Management
1. Risk and Return Balance:
The principle of risk and return balance is pivotal in financial management. Investments that are associated with higher risks generally offer higher returns and vice versa. Managing the fine balance between risk and return ensures that the organization neither exposes itself to undue risk nor misses out on growth opportunities.
2. Financial Planning and Coordination:
Effective financial management requires careful planning and coordination between various financial activities. From budgeting to forecasting and financial reporting, the integration and alignment of these activities form the backbone of a well-managed financial system.
3. Liquidity and Profitability:
Ensuring liquidity is essential for meeting short-term obligations, while profitability focuses on generating returns over the long term. Striking the right balance between liquidity and profitability is a complex task that requires understanding the organization's financial position and market dynamics.
4. Capital Structure Consideration:
The choice between debt and equity in financing an organization's operations is vital. The capital structure must be designed to maximize the value of the firm while considering the cost of capital and the level of financial risk.
5. Ethical Considerations:
Financial management must adhere to ethical principles, ensuring transparency, integrity, and adherence to legal and regulatory standards. Ethical financial practices build trust among stakeholders and contribute to the organization's reputation and success.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation:
Ongoing monitoring and evaluation of financial activities and performance against the set goals and benchmarks help identify improvement areas and implement corrective actions when necessary.
7. Technology Integration:
With the advent of modern technology, financial management tools and software have become essential. Leveraging technology allows for more accurate data analysis, efficient processing, and real-time decision-making.
Read also: 9 Fundamental Accounting Principles for Small Businesses
Fields of Financial Management
Financial management encompasses a broad array of fields where it can be applied, including:
1. Investment Management: Focuses on selecting suitable investments and making decisions related to the composition and distribution of the investment portfolio.
2. Accounting Management: Concerned with preparing and analyzing financial reports and ensuring compliance with accounting standards.
3. Tax Management: Linked to planning and optimizing tax obligations in accordance with local laws and regulations.
4. Cash Management: Works on controlling liquidity and efficiently managing cash and credits.
5. Working Capital Management: Aims at controlling short-term resources to ensure the effective operation of the organization.
6. Financial Risk Management: Deals with analyzing, evaluating, and mitigating financial risks.
These fields provide a framework for organizations to manage their financial resources in an integrated and coordinated way, promoting financial stability and achieving growth.
Objectives of Financial Management
Financial management seeks to achieve a set of primary objectives that promote financial stability and growth, including:
1. Profitability Achievement: Ensuring profits are made through investments and operational activities.
2. Liquidity Assurance: Effectively managing cash to ensure obligations are met when they fall due.
3. Shareholder Value Enhancement: Increasing the value of shares and shareholders' wealth through effective financial control.
4. Risk Management: Identifying, managing, and controlling financial risks.
5. Sustainable Development: Working towards growth while maintaining resources and sustainability.
6. Compliance with Laws and Regulations: Ensuring adherence to local and international laws and regulations.
These objectives guide all aspects of financial management and determine the general direction of the organization.
Read more: The 5 Most Common Auditing Techniques Simply Explained
Financial Management Strategies:
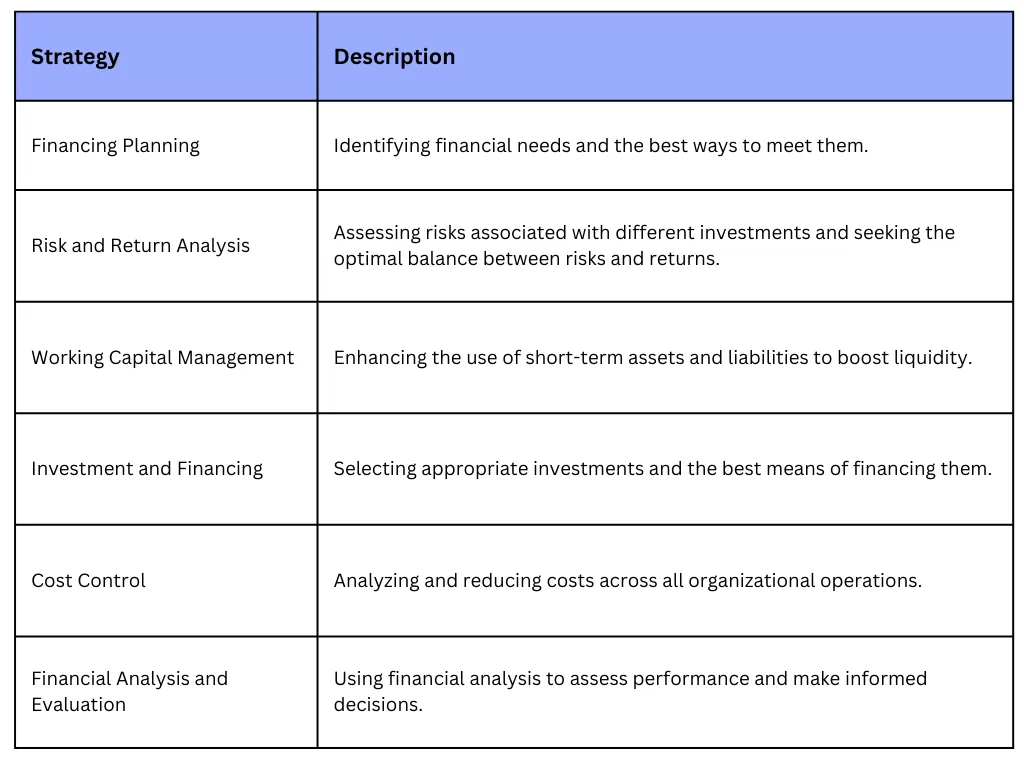
Tips for Organizing Financial Management
Financial management requires precise organization and coordination, and the following tips can be helpful:
- Adhere to Accounting Standards: Ensure compliance with local and international accounting standards and laws.
- Focus on Training and Development: Encourage continuous learning and skill development within the financial management team.
- Utilize Proper Reporting Tools: Provide regular reports that clearly and accurately reflect the financial position.
- Manage Relationships with Financing Entities: Build strong relationships with banks, lenders, and other financial entities.
- Plan for Financial Crises: Prepare plans to deal with any potential financial crises.
These tips offer a practical and focused perspective on organizing financial management and continually working to improve it.
Conclusion
In the face of growing financial challenges that businesses and organizations encounter in our contemporary world, financial management becomes not merely a means to control funds but a strategic pivot that can determine an organization's success or failure. Through effective strategizing, risk assessment, cost control, and adherence to accounting standards, financial stability can be enhanced, and organizational goals achieved. However, it must be noted that financial management requires continual flexibility and innovation to adapt to the constant changes in the business environment. The success of financial management depends on a profound understanding of its tools and techniques, as well as the ability to execute them effectively and responsibly. If managed correctly, financial management can be the driving force behind success and growth, strengthening an organization's sustainability and resilience in the long term.
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.


.png?alt=media)










