What Is Auditing In Accounting And Finance?

Auditing refers to examining companies’ financial reports and statements following a regulatory framework and rules. Auditing is necessary and often even mandatory, so knowing its implications is crucial for accountants and managers alike—read on to find out everything about the matter.
What Is Auditing? Audit Definition Explained
What Is Auditing? Audit Definition Explained
In most contexts, "auditing" refers to examining a company's financial statements.
An impartial study and assessment of an organization's financial statements constitute a financial audit.
The purpose of an audit is to ensure that an organization's financial records are honest and accurate.
A qualified employee of the organization or an independent firm of Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) from the outside can carry out the audit. Depending on that, an audit can be done internally or externally.
Main Takeaways
- Audits may be broken down into two primary categories: external audits and internal audits.
- An auditor's opinion is often provided in the audit report after completing an external audit. Certified Public Accountants (CPA) typically carry out these audits.
- An unqualified audit opinion, also known as a clean audit opinion, indicates that the auditor did not find any significant inaccuracies in the financial statements throughout his or her examination of the statements.
- Both a study of a company's financial statements and an examination of its internal controls can be included in an external audit.
- Internal audits are a management technique that may be used to improve an organization's processes and internal controls.
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.
Auditing In Accounting And Finance Simply Explained
An annual audit of a company's financial accounts, including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement is standard practice for virtually all businesses.
As part of the debt covenants that they impose, lenders frequently want to see the findings of an external audit once a year.
Because of the overwhelming motivations to purposefully misstate financial information in an effort to commit fraud, certain businesses are subject to regulatory requirements that require them to undergo audits.
Most publicly listed firms are required to assess the efficiency of the internal controls they have implemented.
The Worldwide Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB) are responsible for establishing a different group of international guidelines, which they refer to as the International Standards on Auditing (ISA).
Auditing Types Explained
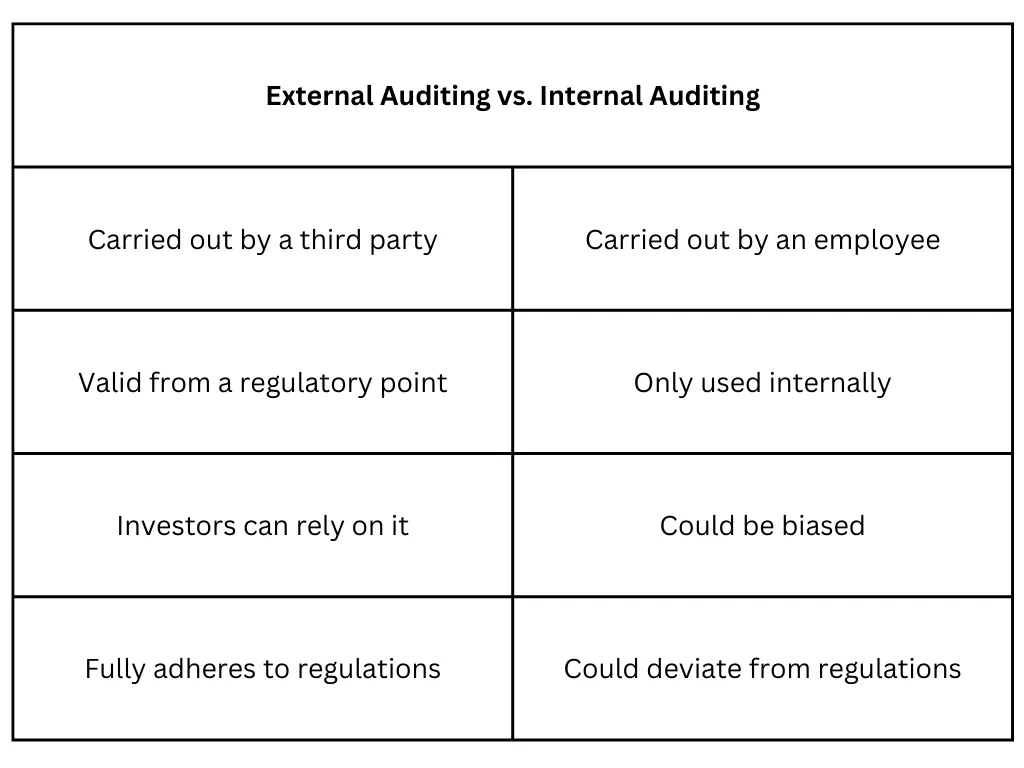
External Audits
Audits conducted by third parties from the outside can be of tremendous assistance in eliminating any potential for bias when evaluating the current health of a company's financials.
Financial statement audits are conducted to determine whether the statements include any significant inaccuracies.
Users of financial statements might have faith that the financial statements are accurate and comprehensive when an auditor delivers an unqualified opinion, also known as a clean opinion.
Therefore, external audits make it possible for stakeholders to make better decisions that are more informed about the organization being audited.
External auditors adhere to a different set of criteria than those utilized by the firm or organization that employs them to perform the auditing work.
The idea of independence on the part of the external auditor is the primary distinction that can be drawn between an internal and an external audit.
When outside parties carry out audits, the auditor's opinion that is expressed on the items being audited (such as a company's financials, internal controls, or a system) can be honest without affecting the daily work relationships that occur within the company.
Internal Audits
Internal auditors are often engaged by the firm or organization being audited, and the ensuing audit report is typically presented directly to management as well as the board of directors.
Although they are not employed directly by the firm being audited, consultant auditors make use of the company's standards rather than a distinct set of standards.
When a company does not have the resources available internally to audit specific aspects of its operations, it will hire this kind of auditor to perform the audit on its behalf.
The findings of the internal audit are analyzed and utilized in the process of making managerial adjustments and improving internal controls.
An internal audit is performed to ensure compliance with laws and regulations, helping to maintain accurate and timely financial reporting and data collecting and ensuring that the audit is carried out promptly.
It is also beneficial to management since it identifies deficiencies in internal control or financial reporting before external auditors review those defects. This helps avoid potential problems.
Read also: The 5 Most Common Auditing Techniques - Simply Explained.
The Conclusion
Auditing is a necessary course of action that consists of examining a company’s financial statements and reports based on a set of predetermined criteria often set by regulators.
Based on the auditor and the purpose of the audit, there are two types of auditing: internal and external auditing.
If you’d like to know more about financial reporting and all the must-know facts of the matter, check out our related article now—see you there!
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.
Use Wafeq - an accounting system to keep track of debits and credits, manage your inventory, payroll, and more.





.png?alt=media)








