How to calculate asset turnover ratio and what is its importance?

How well is your company turning its assets into revenue? This simple yet powerful question lies at the heart of the most important efficiency metrics in financial analysis: the Asset Turnover Ratio. Whether evaluating performance, preparing for investor discussions, or comparing operations across time, this ratio signals clearly how productively companies' assets are being used. In this article, we’ll explore how to calculate it, when to use it, and why it matters.
Asset Turnover Ratio – Definition and Formula
The Asset Turnover Ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate revenue. It answers a fundamental operational question: How many Riyals of sales are generated for every Riyal invested in assets? The ratio is usually calculated annually, but can also be applied quarterly or monthly, depending on the financial reporting cycle.
Formula:
Formula:
Asset Turnover Ratio =
Net Sales ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
Average Total Assets
- Net Sales: Total revenue from operations, excluding returns, discounts, and allowances.
- Average Total Assets: The average of total assets at the beginning and end of the period.
Average Total Assets = Total Assets at Beginning of Period + Total Assets at End of Period ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ 2
How to Calculate It – Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding the Asset Turnover Ratio is easier when we walk through the calculation process. Here's a simple step-by-step guide using a fictional company.
Step 1: Determine Net Sales
Step 1: Determine Net Sales
Let’s say Al-Fahad Trading Company reported the following for the year 2024:
Gross Revenue: SAR 8,200,000
Sales Returns and Allowances: SAR 200,000
Net Sales = SAR 8,200,000 – 200,000 = SAR 8,000,000
Step 2: Calculate Average Total Assets
Step 2: Calculate Average Total Assets
Total Assets at the beginning of 2024: SAR 5,000,000
Total Assets at the end of 2024: SAR 7,000,000
Average Total Assets = (5,000,000 + 7,000,000) ÷ 2 = SAR 6,000,000
Step 3: Apply the Formula
Step 3: Apply the Formula
Asset Turnover Ratio= 8,000,000 ÷ 6,000,000 =1.33
Interpretation:
An Asset Turnover Ratio of 1.33 means that for every 1 riyal invested in assets, the company generated 1.33 riyals in sales during the year.
This indicates a relatively efficient use of assets, especially when compared to industry benchmarks.
What Does the Ratio Indicate?
The Asset Turnover Ratio does more than quantify efficiency; it provides insight into how well management utilizes the company's assets to support revenue generation.
High Asset Turnover Ratio
A high ratio typically suggests:
- Efficient asset utilization.
- Strong operational performance.
- Lean asset base relative to revenue.
This is common in retail and FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods) sectors, where asset bases are lighter and sales volumes are high. Example: A ratio of 2.5 indicates that the company generates SAR 2.5 in sales for every SAR 1 invested in assets.
Low Asset Turnover Ratio
A low ratio may indicate:
- Underutilized assets.
- Inefficient operations.
- Over-investment in assets that do not generate proportional returns.
Industries with capital-intensive operations, like manufacturing or utilities, may naturally have lower ratios due to large fixed asset investments. A ratio of 0.5, for instance, could signal that SAR 1 in assets is generating only SAR 0.50 in sales.
Asset Turnover Ratio Use in Trend Analysis and Comparisons
The ratio becomes more meaningful when:
- Tracked over time to identify trends in operational efficiency
- Compared across peers within the same industry
- Combined with profitability ratios like ROA (Return on Assets) or Net Profit Margin for deeper insights
Why Is the Asset Turnover Ratio Important?
The Asset Turnover Ratio is more than a performance metric; it’s a strategic indicator that reflects how well a company converts its resources into value. The ratio helps all stakeholders, CFOs, analysts, investors, and auditors understand how well a company manages its resources to drive top-line growth.
- Evaluates Operational Efficiency as the ratio measures the effectiveness of asset usage in generating revenue, allowing finance teams to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
- Supports Strategic Decision-Making as a declining ratio may prompt management to reassess asset-heavy investment, improve working capital utilization, and adjust pricing or production strategies.
- Assists in Industry Benchmarking. Investors and analysts often compare this ratio across industry peers to gauge competitiveness and operational excellence.
- Links to Profitability Although it doesn’t measure profits directly, a higher turnover often correlates with improved Return on Assets (ROA), better capital allocation, and increased shareholder value.
- Useful for Lenders and Creditors, as Banks and financial institutions may use the ratio as part of credit assessments, especially to evaluate asset-heavy businesses and repayment ability.
Limitations of the Asset Turnover Ratio
While the Asset Turnover Ratio is a valuable efficiency indicator, it should not be interpreted in isolation. Like all financial metrics, it has limitations that professionals must consider in context.
- Does Not Reflect Profitability A high ratio may indicate efficient asset use, but does not guarantee profitability. A company can generate high sales with very low or even negative margins.
- Affected by Industry Differences Different industries have vastly different asset structures. For example, a supermarket may have a ratio above 3, and a utility company may have a ratio below 0.5. This makes cross-industry comparisons misleading.
- Can Be Distorted by Seasonality In seasonal businesses (like retail or tourism), asset levels and revenues fluctuate heavily throughout the year. A single annual figure may not capture true performance.
- Relies on Accurate Asset Valuation The ratio depends on the accuracy of reported assets. Overstated or outdated asset values (e.g., undepreciated fixed assets) can significantly distort the ratio.
- Ignores Asset Quality and Type It treats all assets equally, without accounting for differences in asset liquidity, productivity, or strategic importance (e.g., cash vs. machinery or patents).
Best Practice:
Best Practice:
Always interpret the Asset Turnover Ratio in conjunction with other financial metrics such as:
- Return on Assets (ROA).
- Gross Margin.
- Fixed Asset Turnover for a complete picture.
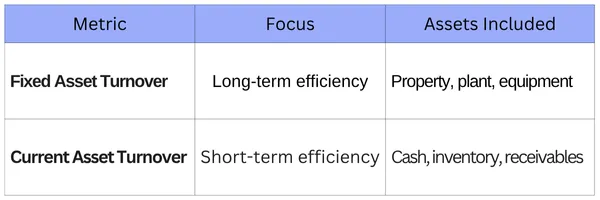
The Key Difference Between Fixed Asset Turnover and Current Asset Turnover
The Asset Turnover Ratio gives a broad view of how efficiently a company utilizes all its assets. The ratio can be useful for zooming in on specific asset categories, fixed and current assets, to gain more focused insights.
Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio
This ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its long-term fixed assets (like machinery, buildings, and equipment) to generate sales. It is common in capital-intensive industries (e.g., manufacturing, telecom) and helps assess the return on heavy infrastructure investments. A low fixed asset turnover could signal underutilized assets or overinvestment in property, plant, and equipment.
Formula:
Formula:
Fixed Asset Turnover = Net Sales ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ Average Fixed Assets
Current Asset Turnover Ratio
This ratio measures the efficiency of a company’s short-term assets (like cash, receivables, and inventory) in generating sales. It is particularly relevant in retail, wholesale, and trading businesses, and indicates how quickly working capital is being converted into revenue. A very high ratio may indicate narrow working capital management, while a low ratio may refer to slow inventory turnover or inefficiencies in receivables.
Formula:
Formula:
Current Asset Turnover =
Net Sales _______________________________
Average Current Assets
Also Read: Current Assets vs. Noncurrent Assets.
The Asset Turnover Ratio is more than a technical metric. It reflects how well a company transforms its assets into value. For CFOs, accountants, analysts, and investors alike, this ratio is a reliable tool to assess operational efficiency, support strategic decision-making, and benchmark performance within an industry. However, like any financial indicator, it must be analyzed in context. Complementing it with other ratios such as ROA, Gross Margin, and Working Capital Turnover provides a more complete and accurate financial picture.
FAQs about Asset Turnover Ratio
What does the Asset Turnover Ratio measure?
The Asset Turnover Ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its total assets to generate revenue. It reflects the amount of sales generated per riyal of assets, indicating how the company is productive in using its resources.
How are assets measured in accounting?
Assets are measured based on their value in financial terms, typically using historical cost, fair value or net realizable value, depending on the type of asset and the applicable accounting standard. For example:
- Fixed assets are usually recorded at historical cost minus accumulated depreciation.
- Financial assets may be measured at fair value if required by standards like IFRS.
What is "Asset Measurement" in accounting?
Asset measurement refers to determining the monetary value process assigned to an asset in the financial statements. It ensures that assets are reported fairly and accurately, using methods like historical cost, current cost, realizable value, and fair value. This is crucial for transparent financial reporting and compliance with standards like IFRS or SOCPA.
What is Standard No. 10 for Fixed Assets (SOCPA)?
Standard No. 10 issued by SOCPA (Saudi Organization for Chartered and Professional Accountants) governs the accounting treatment of fixed assets. It includes capitalization criteria, depreciation methods, useful life, impairment recognition, disposal, and derecognition rules. This standard ensures consistency and clarity in property reporting, plant, and equipment in Saudi Arabia.
Wafeq makes it easy to calculate and monitor key ratios such as Asset Turnover, automatically and in real-time.
Wafeq makes it easy to calculate and monitor key ratios such as Asset Turnover, automatically and in real-time.
Stay compliant, gain insights, and make smarter decisions.





.png?alt=media)









