Understanding UAE E-Invoicing: A Practical Guide for Companies

To help you navigate the transition of e-invoicing in the UAE, this guide focuses on the most important points every business should understand before e-invoicing becomes mandatory in the UAE.
Key Takeaways from this guide are:
- Understand the UAE e-invoicing legal framework and official system requirements.
- Learn who must comply and when, based on phased implementation timelines.
- Know the exact technical and operational rules (formats, transmission, storage)
- Identify penalties and compliance risks and how to avoid them.
- Prepare your systems and processes ahead of mandatory deadlines.
- See how Wafeq enables compliant, audit-ready e-invoicing.
E-Invoicing in the UAE: Compliance, Digitization, and Business Readiness
The UAE Ministry of Finance has confirmed its intention to implement a nationwide e-invoicing framework based on international best practices, aligning the country with global digital tax ecosystems. Once implemented, businesses will be required to issue and receive invoices in a structured electronic format that enables seamless exchange, validation, and auditability.
For finance teams and business owners, understanding how UAE e-invoicing works, who it applies to, and how to prepare is no longer optional. Early awareness and system alignment will play a key role in ensuring compliance, operational continuity, and long-term efficiency.
In recent years, the United Arab Emirates government has actively promoted increased digitization in the public sector. This includes the successful introduction of a fully digitized public procurement platform (DPP) and Dubai's pioneering initiative to become a completely paperless government in 2021.
What Is E-Invoicing? (And What It Is Not)
E-invoicing refers to the creation, exchange, and storage of invoices in a structured electronic format that can be automatically processed by accounting systems and, where required, tax authorities. Unlike traditional invoices, e-invoices are designed for machine readability, not just human viewing.
In the context of the UAE’s upcoming framework, an e-invoice is not simply a digital copy of a paper invoice. It must contain standardized data fields and follow a defined structure—typically XML—allowing invoices to be validated, exchanged, and audited electronically.
What E-Invoicing is
- A structured electronic invoice generated directly from an accounting or ERP system.
- An invoice that can be automatically read and processed without manual data entry.
- A format that supports regulatory compliance, audit trails, and data integrity.
What E-Invoicing Is Not?
- A PDF invoice sent by email.
- A scanned paper invoice.
- An image file or unstructured document that requires manual input.
While PDFs and scanned invoices may be digital in form, they do not meet the technical or regulatory definition of e-invoicing. They lack standardized data structures and can't support automated validation or reporting.
Why This Distinction Matters in the UAE
The UAE e-invoicing framework is designed to enable seamless data exchange between suppliers, buyers, and regulatory bodies. This requires invoices to be issued in a structured format that systems can interpret consistently. For businesses, this means that existing invoicing practices, such as emailing PDFs or uploading scanned documents, will not be sufficient once e-invoicing becomes mandatory. Accounting systems must be capable of generating compliant e-invoices from the source of transaction data.
Legal Framework Governing UAE E-Invoicing
The UAE e-invoicing initiative is governed by a clear legal and regulatory framework issued by the Ministry of Finance, ensuring alignment with international standards and enforceable compliance across all business sectors. The country's recognition of e-invoice exchange between consenting parties and the implementation of the DPP exemplifies its commitment to digital transformation.
On January 1, 2018, the UAE introduced Value Added Tax (VAT) at a standard rate of 5%, marking a significant shift in its fiscal policy. This move was part of a broader strategy to diversify the economy and reduce dependence on oil revenues. Crucial to this change was the recognition of digital or electronic invoices as valid under the UAE's VAT law. Federal Decree-Law No. 8 of 2017 on VAT and Federal Law No. 1 of 2006 on Electronic Commerce and Transactions laid the groundwork for this digital transformation.
Read more: How Wafeq help SMEs to balance their books?
Understanding the Federal Law No. 1 of 2006
The Federal Law No. 1 of 2006 is a cornerstone in the UAE's digital landscape. It gives legal recognition to electronic records, documents, and signatures, particularly in the realm of e-commerce and transactions. This law establishes uniform rules and standards for authenticating all electronic communications and e-invoicing through electronic signatures, ensuring their validity and legal standing.
Towards Mandatory B2B e-Invoicing
Reflecting this digital momentum, on July 11th, 2023, the UAE Ministry of Finance announced plans to implement an 'e-billing' solution. This initiative, started in July 2025, introduced a mandatory B2B e-invoicing regime, marking a significant shift towards the complete digitalization of financial transactions.

The Ministry of Finance’s eProcurement System
The Ministry of Finance (MoF) has implemented an eProcurement system, a significant step towards digital transformation. This system automates the entire purchasing cycle until fee payment completion. It enables vendors to participate in online tenders and auctions, follow up on purchase orders, and submit digital invoices, fostering a more efficient and transparent procurement process.
Read more: All you need to know about VAT in UAE.
Telecommunications Regulatory Authority’s e-Invoicing System
Mirroring MoF's initiatives, the Telecommunications Regulatory Authority has established an electronic invoicing system. This platform allows contracted suppliers to submit invoices electronically, ensuring a streamlined process for managing financial dues, purchase orders, and contracts.
Official System Name: Electronic Invoicing System (EIS)
- The UAE’s nationwide e-invoicing initiative is officially referred to as the Electronic Invoicing System (EIS).
- EIS establishes the technical, operational, and compliance requirements for issuing, transmitting, and storing electronic invoices in the UAE.
- All references to “e-invoicing” in UAE regulations relate to compliance with the Electronic Invoicing System (EIS).
Ministerial Decision No. 243 of 2025 – Scope and Obligations
Ministerial Decision No. 243 of 2025 defines the scope of application and core obligations under the Electronic Invoicing System (EIS).
This decision outlines:
- Which taxable persons are required to comply with e-invoicing?
- The obligation to issue and receive invoices in a structured electronic format.
- The requirement to use approved technical channels for invoice exchange.
- General responsibilities of invoice issuers and recipients.
In practice, this decision establishes who must comply and how e-invoicing must function at a high level.
In practice, this decision establishes who must comply and how e-invoicing must function at a high level.
Ministerial Decision No. 244 of 2025 – Implementation Timeline and Deadlines
Ministerial Decision No. 244 of 2025 outlines the phased implementation timeline for the Electronic Invoicing System (EIS). It defines:
- Mandatory implementation phases by business category.
- Official deadlines for system readiness.
- Timing for enforcement and penalties.
- Transitional arrangements for affected businesses.
This decision forms the legal basis for the phased rollout approach, giving businesses time to prepare while ensuring nationwide adoption.
This decision forms the legal basis for the phased rollout approach, giving businesses time to prepare while ensuring nationwide adoption.
Dubai’s Paperless Strategy 2021
A landmark initiative, Dubai's Paperless Strategy 2021, aims to eliminate over 1 billion pieces of paper annually used in government transactions. This strategy not only saves time and resources but also significantly reduces the environmental impact. By digitizing all internal and customer-facing transactions, the government sets a new standard for operational efficiency.
Is E-Invoicing Mandatory in the UAE? _ Current Status and Timeline
As of today, e-invoicing is not yet mandatory in the UAE, but it is officially confirmed and actively under development by the UAE Ministry of Finance. The government has announced a phased rollout of a nationwide e-invoicing system as part of its broader digital transformation and tax compliance strategy.
The UAE’s approach is proactive rather than reactive. Instead of introducing e-invoicing abruptly, the Ministry of Finance has outlined a gradual implementation roadmap, allowing businesses, software providers, and accounting firms time to prepare their systems and processes.
Official Status of UAE E-Invoicing
- The UAE Ministry of Finance has confirmed the adoption of a federal e-invoicing framework.
- The system will be based on international standards, specifically the Peppol network.
- E-invoicing will support VAT compliance and future tax reporting requirements.
- Implementation will follow a phased approach, not a single enforcement date.
Who Needs to Comply with UAE E-Invoicing
UAE e-invoicing will primarily apply to:
- VAT-Registered Businesses Any business registered for VAT in the UAE will be required to issue and receive compliant e-invoices once the mandate applies to its category. This includes businesses that issue taxable supplies at standard or zero rates.
- Large Businesses Businesses exceeding the revenue thresholds defined by the Ministry of Finance will be included in the earliest mandatory phases. These entities are expected to have the systems and resources needed for early adoption and pilot participation.
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) SMEs will be brought into scope in later phases of implementation. However, SMEs are strongly encouraged to prepare early, as e-invoicing requirements will apply regardless of business size once mandatory.
- Free Zone Companies Free zone entities are not exempt from e-invoicing requirements if they:
- Are VAT-registered, or
- Engage in taxable B2B transactions within the UAE
Free zone status doesn't relieve the obligation to comply with federal tax and invoicing regulations.
Free zone status doesn't relieve the obligation to comply with federal tax and invoicing regulations.
5. Government and Semi-Government Entities Government entities involved in B2G (Business-to-Government) transactions will be included in dedicated implementation phases to ensure standardized invoicing across public-sector procurement.
Who is Currently Out of Scope?
At the current stage of implementation:
- B2C transactions are not included in the mandatory e-invoicing scope.
- Certain transaction types may be excluded initially, subject to future regulatory updates.
The Ministry of Finance may extend the scope in later phases as the framework matures.
The Ministry of Finance may extend the scope in later phases as the framework matures.
UAE E-Invoicing Implementation Roadmap (2026–2027)
The UAE’s Ministry of Finance has outlined a phased rollout for e-invoicing, starting with a pilot and voluntary adoption phase from 1 July 2026. Eligible businesses must appoint an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) by the specified deadlines before the e-invoicing obligation becomes mandatory on a staggered basis — starting with large taxpayers on 1 January 2027, followed by smaller businesses on 1 July 2027, and government entities on 1 October 2027.
The phased implementation of e-invoicing in the UAE is governed by Ministerial Decision No. 244 of 2025, which defines the mandatory rollout timeline, compliance deadlines, and transitional arrangements under the Electronic Invoicing System (EIS).
.png?alt=media)
Notes:
Notes:
- Businesses can voluntarily adopt e-invoicing starting on July 1, 2026, even before mandatory dates begin.
- All categories must appoint an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) by the specified deadline to be technically ready.
- E-invoicing in B2C is currently excluded but may be brought into scope with future decisions.
Who Should Prepare Now?
Even before the mandate becomes effective, businesses are strongly encouraged to prepare if they:
- Are VAT-registered.
- Issue a high volume of invoices.
- Operate across multiple entities or locations.
- Work with government or large corporate buyers.
- Manage invoicing on behalf of multiple clients (accounting firms)
Pro Tip:
Pro Tip:
Even if your phase is in the future, starting early helps your team, your systems, and your cash flow stay fully compliant and error-free.
Why Early Adoption of UAE E-Invoicing Matters
Although mandatory implementation will be enforced in phases, early adoption of e-invoicing offers clear operational and compliance advantages for UAE businesses.
Early adopters gain sufficient time to:
- Test current invoice workflows and data accuracy.
- Align internal processes with regulatory requirements.
- Confirm accounting system readiness for structured e-invoicing.
- Understand ASP appointment requirements and timelines.
- Train finance and accounting teams.
- Resolve system integration issues before enforcement deadlines.
From a compliance perspective, early readiness reduces the risk of last-minute disruptions, invoice rejections, or reporting errors once e-invoicing becomes mandatory. Operationally, it allows businesses to shift from manual invoicing practices to automated, structured invoice management at a controlled pace.
From a compliance perspective, early readiness reduces the risk of last-minute disruptions, invoice rejections, or reporting errors once e-invoicing becomes mandatory. Operationally, it allows businesses to shift from manual invoicing practices to automated, structured invoice management at a controlled pace.
In jurisdictions where e-invoicing has already been implemented, businesses that adopted early experienced smoother transitions and fewer compliance issues compared to those that waited until enforcement dates.
What is an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) and Why is It Required?
Under the UAE e-invoicing framework, businesses will not connect directly to buyers or tax authorities on their own. Instead, they must issue and receive e-invoices through an Accredited Service Provider (ASP).
An ASP is a Ministry of Finance–approved provider that:
- Connects businesses to the national e-invoicing network.
- Ensures invoices follow the required structured format.
- Performs validation and secure exchange of e-invoices.
- Maintains compliance with technical and regulatory standards.
The requirement to appoint an ASP ensures:
- Standardization of invoice data across the UAE.
- Secure and reliable invoice exchange.
- Consistent compliance enforcement.
- Reduced technical complexity for businesses.
For this reason, the UAE roadmap includes mandatory ASP appointment deadlines ahead of each implementation phase, giving businesses time to complete technical onboarding before e-invoicing becomes compulsory.
How the Phased Implementation Approach Helps Businesses Prepare
The UAE has adopted a phased e-invoicing rollout to minimize disruption and allow businesses to prepare based on size, complexity, and transaction volume.
This approach benefits businesses by:
- Allowing gradual system upgrades rather than abrupt changes.
- Giving large businesses time to pilot and stabilize processes.
- Enabling SMEs to learn from early adopters.
- Providing software vendors and accounting firms time to scale readiness.
What Happens If E-Invoicing Deadlines Are Missed?
Once e-invoicing becomes mandatory for a specific business category, as specified in Ministerial Decision No. 244 of 2025, failure to comply may result in regulatory and operational consequences.
Potential risks include:
- Non-compliant invoices are being rejected by buyers.
- Inability to issue valid tax invoices.
- Increased audit exposure.
- Administrative penalties under UAE tax regulations.
- Disruption to cash flow due to delayed or invalid invoicing.
UAE E-Invoicing Penalties & Fines (Under Cabinet Decision No. 106 of 2025)
Because e-invoicing is closely tied to VAT compliance and future digital tax reporting, missed deadlines may also affect a business’s broader tax compliance position. Here are the penalties ones that apply only after the mandatory dates.
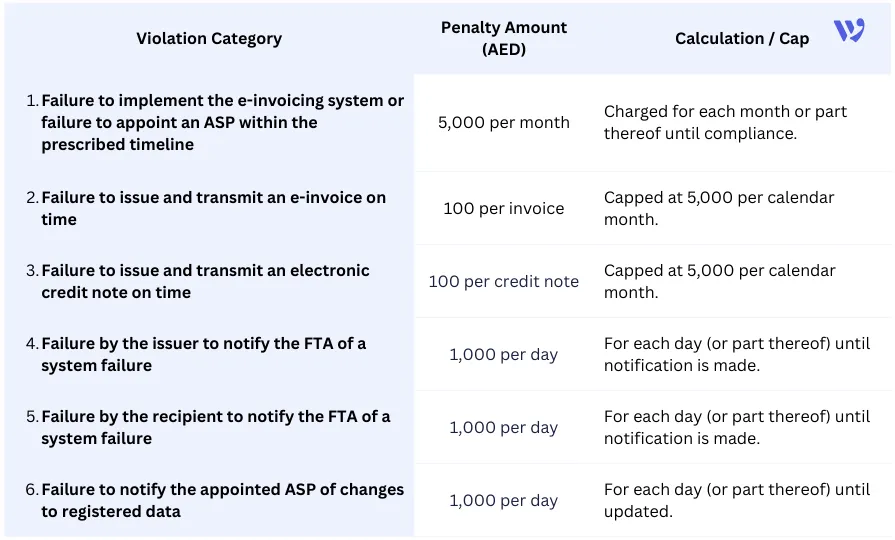
Regulatory Note
Regulatory Note
These penalties apply only after the mandatory compliance dates for each business category (e.g., large taxpayers from January 1, 2027, and all other VAT-registered businesses later). No fines apply during voluntary adoption phases.
The Federal Tax Authority applies penalties proportionally, with escalating enforcement for repeated or prolonged violations, in line with the objectives of Ministerial Decision No. 243 of 2025. For this reason, appointing an accredited service provider and ensuring system readiness before mandatory dates is critical for uninterrupted operations.
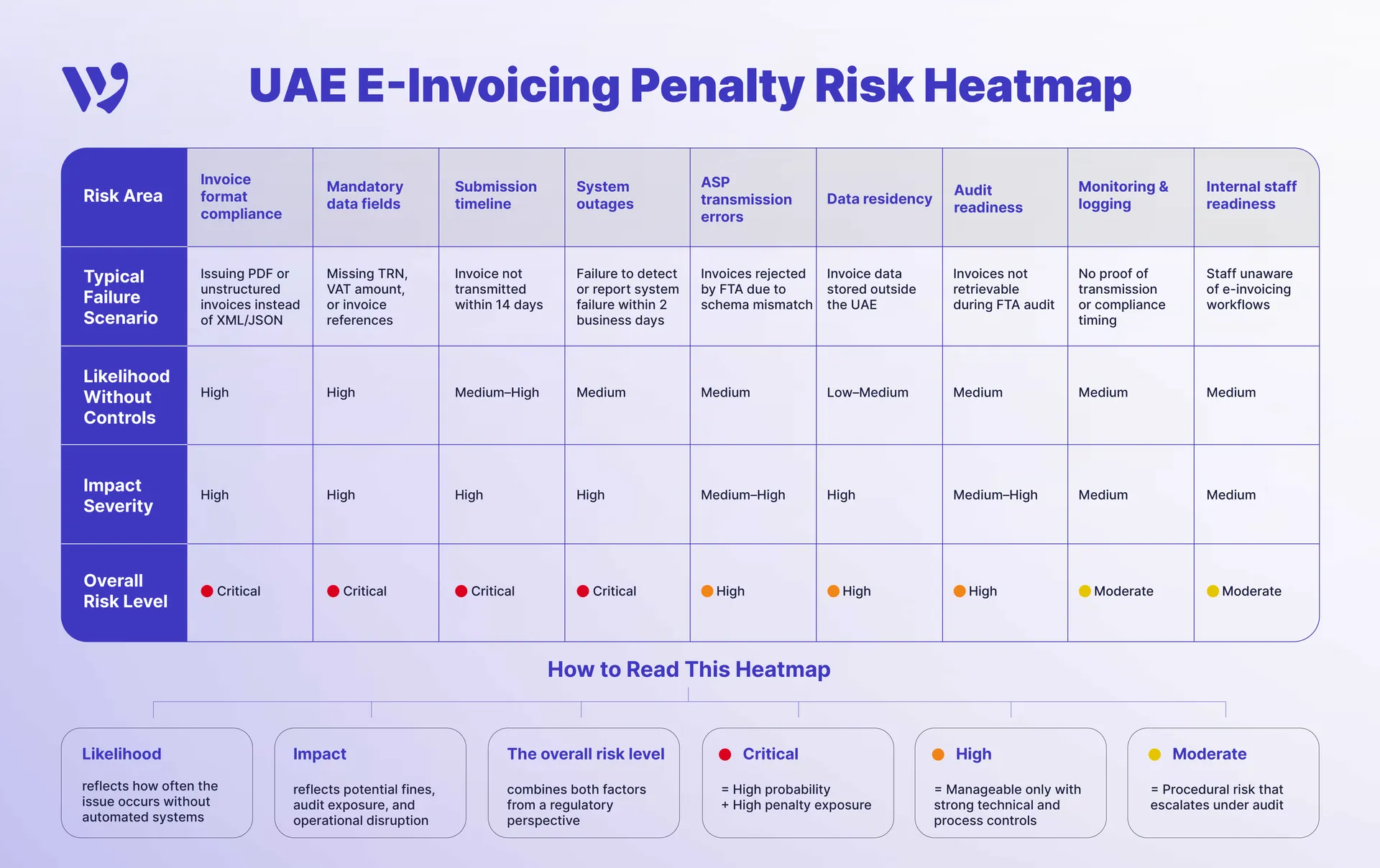
UAE E-Invoicing Penalty Risk Heatmap
How UAE E-Invoicing Works (End-to-End Process)
The UAE e-invoicing system is designed to enable secure, standardized, and automated exchange of invoice data between suppliers, buyers, and the national e-invoicing network. Unlike traditional invoicing, the process relies on structured data, system validation, and certified intermediaries.
Below is a simplified, end-to-end view of how e-invoicing will work in the UAE.
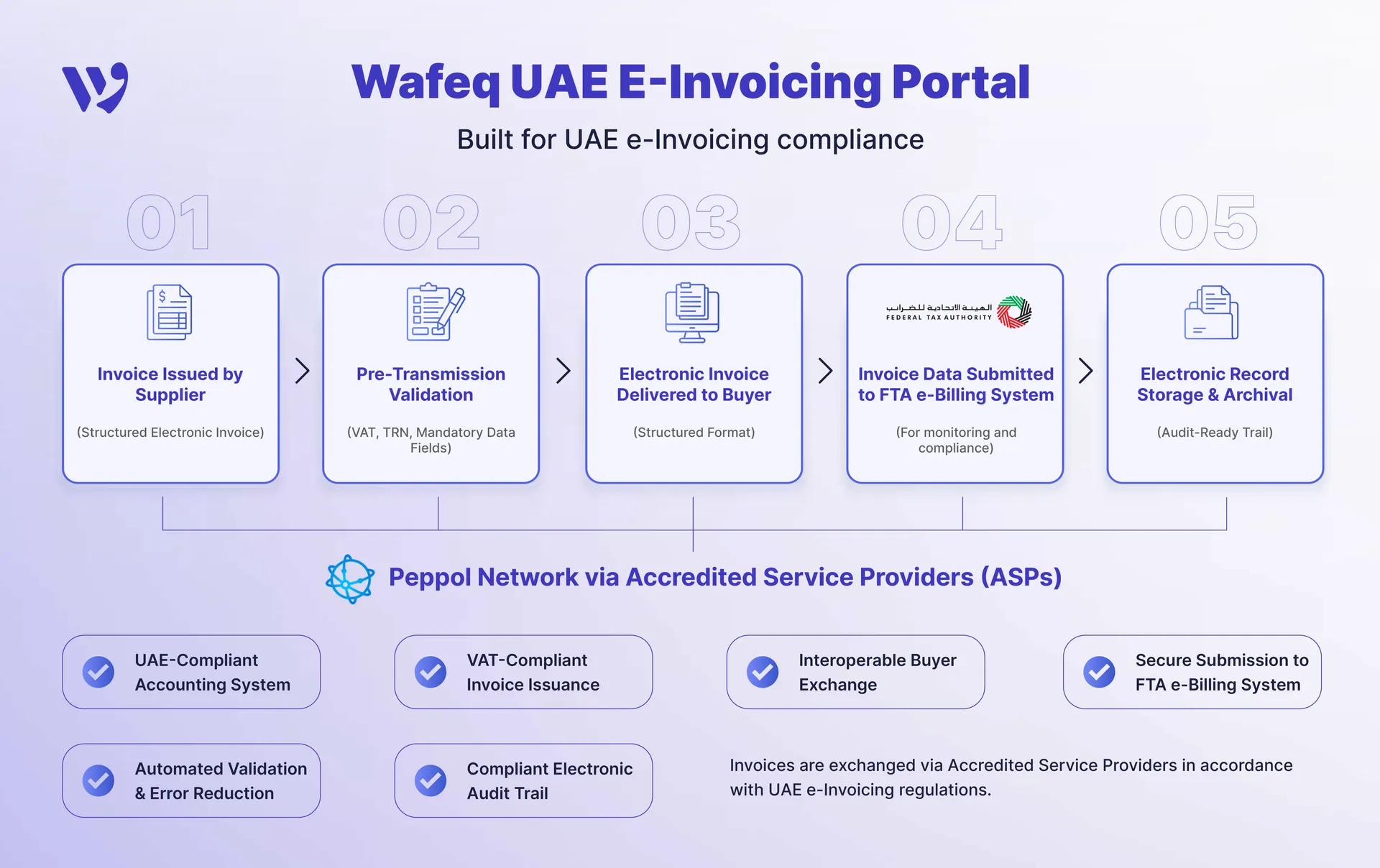
Step 1: Invoice Creation in the Accounting System
The process begins when a supplier creates an invoice in its accounting or ERP system. Instead of generating a PDF or paper invoice, the system produces a structured electronic invoice, typically in XML format, containing all mandatory invoice data.
This includes:
- Supplier and buyer details.
- VAT registration numbers.
- Invoice number and date.
- Line item details.
- Tax amounts and totals.
At this stage, the accuracy of master data is serious, as incorrect information may result in invoice rejection later in the process.
Step 2: Invoice Validation and Formatting
Once created, the invoice is validated to ensure:
- All mandatory fields are present.
- Data formats comply with UAE technical specifications.
- VAT calculations are accurate.
- Invoice identifiers are unique and consistent.
The invoice is then formatted according to the UAE e-invoicing data model to ensure compatibility across systems.
Step 3: Transmission via an Accredited Service Provider (ASP)
After validation, the e-invoice is transmitted through an Accredited Service Provider (ASP). The ASP acts as a certified intermediary, securely exchanging the invoice with the buyer’s system through the national e-invoicing network.
The ASP ensures:
- Secure delivery.
- Data integrity.
- Compliance with Peppol-based exchange standards.
- Reliable transaction logging.
Step 4: Delivery to the Buyer
The buyer receives the structured e-invoice directly into their accounting or ERP system via their own ASP. This enables:
- Automatic invoice capture.
- Reduced manual data entry.
- Faster invoice processing and approval.
- Improved reconciliation and audit readiness.
Depending on internal workflows, buyers may still receive a human-readable representation (such as a PDF view), but the structured data remains the legally relevant version.
Step 5: Storage and Audit Readiness
E-invoices must be stored electronically in a manner that ensures:
- Data integrity.
- Accessibility for audits.
- Compliance with UAE record retention requirements.
Because invoices are issued in a structured format, businesses can maintain accurate audit trails and respond more efficiently to tax authority inquiries.
UAE E-Invoicing Models Explained (Why the UAE Chose the Peppol Model)
As part of its national e-invoicing initiative, the UAE has adopted a decentralized e-invoicing model based on Peppol framework, an internationally recognized standard for electronic document exchange. This model balances regulatory oversight with business flexibility and scalability.
Understanding the chosen model—and why it matters—is essential for businesses preparing their invoicing systems.
Centralized vs Decentralized E-Invoicing Models
Globally, tax authorities implement e-invoicing using two primary models:
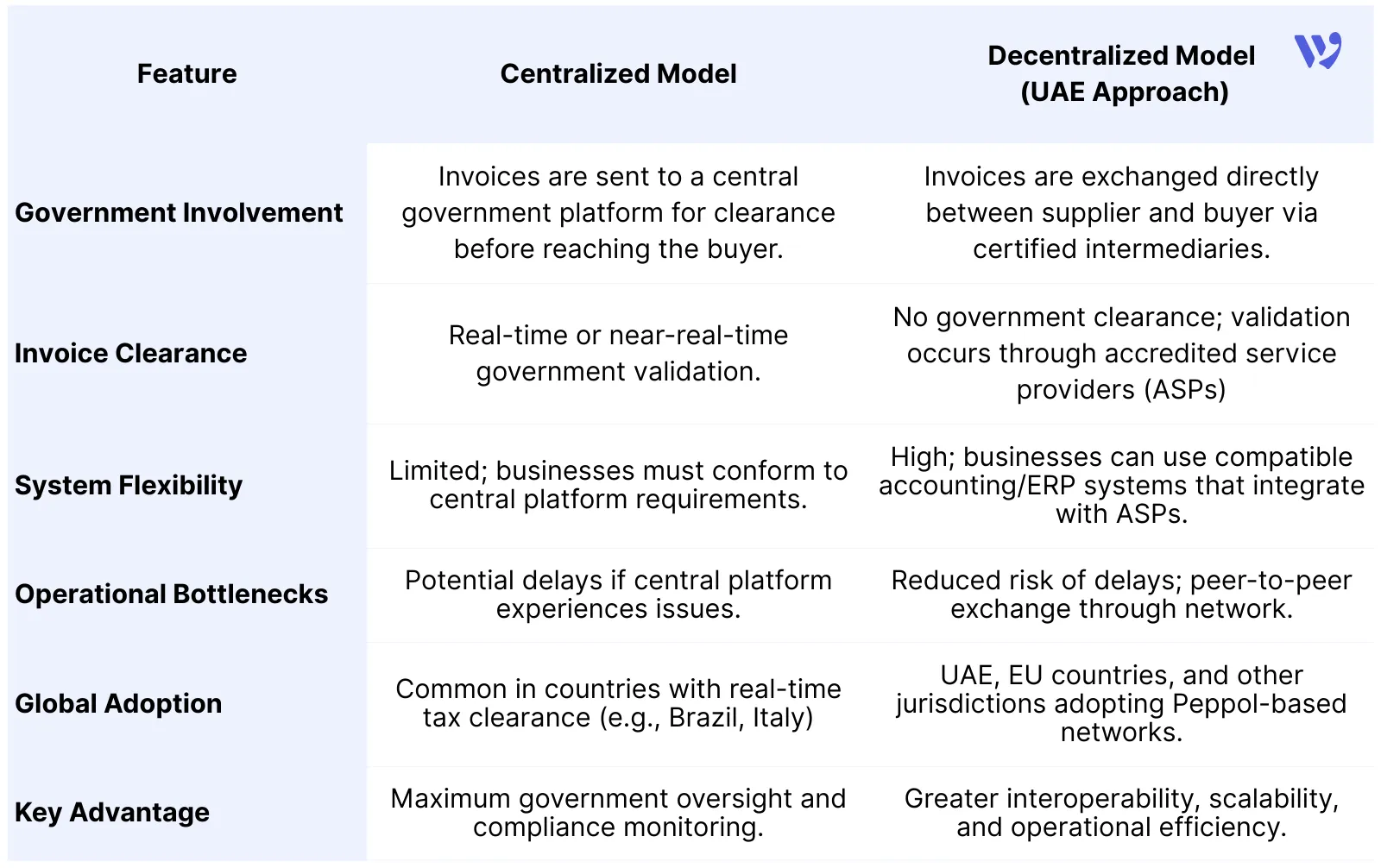
Why the UAE Chose the Peppol-Based Model
The UAE’s e-invoicing framework is built on Peppol (Pan-European Public Procurement Online), a global network used across Europe and multiple international jurisdictions.
Peppol provides:
- A standardized data model for electronic invoices.
- A secure, interoperable exchange network.
- Clear governance and accreditation rules.
- Cross-border compatibility.
By adopting Peppol standards, the UAE ensures that its e-invoicing system aligns with international best practices while remaining adaptable to local tax and regulatory requirements.
Key Components of the UAE Peppol-Based Framework
The UAE e-invoicing ecosystem consists of several interconnected components:
- Businesses (Suppliers and Buyers) Businesses issue and receive structured electronic invoices directly from their accounting systems.
- Accounting and ERP Systems Systems must be capable of generating invoices in the required structured format and supporting automated data validation.
- Accredited Service Providers (ASPs) ASPs act as certified intermediaries, ensuring: - Secure invoice transmission. - Compliance with Peppol standards. - Interoperability between different systems.
- UAE E-Invoicing Network The Peppol-based network enables standardized exchange without requiring a centralized government clearance step.
Benefits of the Peppol Model for UAE Businesses
Adopting a Peppol-based model delivers tangible benefits:
- Interoperability: Businesses can exchange invoices regardless of the accounting system their trading partners use.
- Scalability: The framework supports businesses of all sizes, from SMEs to large enterprises.
- Future readiness: Peppol enables cross-border invoicing and expansion without reengineering systems.
- Operational efficiency: Reduced manual data entry and faster invoice processing.
- Regulatory alignment: Consistent compliance without centralized bottlenecks.
What This Means for Businesses Preparing for Compliance
Under the UAE’s model, businesses are responsible for:
- Using an accounting system capable of generating structured e-invoices.
- Appointing an accredited service provider within the required timeline.
- Ensuring invoice data accuracy and VAT compliance.
Unlike centralized models, compliance in the UAE depends heavily on system readiness and integration, rather than government-side invoice clearance.
Clear Explanation of Accredited Service Provider (ASP) Responsibilities
Under the UAE Electronic Invoicing System (EIS), businesses are required to exchange electronic invoices through Accredited Service Providers (ASPs). ASPs act as the technical and compliance bridge between suppliers, buyers, and the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
Understanding what ASPs actually do helps businesses assess readiness and choose the right accounting and invoicing setup.
Core Responsibilities of an ASP
- Data Mapping to FTA Schema ASPs map invoice data generated by business systems into the FTA-approved structured schema, ensuring all mandatory fields are correctly positioned and formatted.
- Invoice Validation and Error Handling Before transmission, ASPs:
- Validate VAT calculations.
- Check TRNs and mandatory data fields.
- Detect formatting or compliance errors.
3. Data Enrichment ASPs enrich invoice data by applying:
- Standardized tax and business codes.
- Required metadata.
- Digital signatures or security markers (where applicable)
4. Conversion to Structured Formats (XML / JSON) If invoices originate in internal system formats, ASPs convert them into:
- XML or JSON.
- In line with UBL or Peppol PINT standards.
5. Real-Time Transmission to Buyer and FTA ASPs ensure:
- Secure invoice delivery to buyers via the Peppol Network.
- Submission of invoice data to the FTA e-Billing system for monitoring and compliance.
6. Monitoring, Alerts, and Fallback Procedures ASPs provide:
- System monitoring and transmission tracking.
- Alerts for failures or delays.
- Fallback mechanisms during outages.
7. Secure UAE-Based Archival ASPs support:
- Secure storage of structured invoice data،
- UAE-based data residency compliance.
- Long-term, tamper-proof record retention.
How Wafeq Fits Within the UAE E-Invoicing Model
Wafeq is designed to operate seamlessly within the UAE’s decentralized, Peppol-based framework by:
Phase-Based Readiness
Generates structured, VAT-comilant e-invoices for businesses' specific implementation phase.
Automated Validation
Reduces errors and ensures invoices meet FTA requirements from day one.
ASP Integration
Connects with accredited service providers ahead of deadlines for secure exchange.
Audit Trail & Reporting
Keeps audit-ready records aligned with UAE tax requirements for inspections and compliance checks.
Exact Data and Technical Format Requirements for UAE E-Invoicing
To comply with UAE e-invoicing regulations, all electronic invoices must include a set of mandatory data fields. These fields ensure that invoices are legally valid, VAT-compliant, and machine-readable for automatic processing by buyers and tax authorities.
Structured e-invoices help reduce errors, accelerate invoice processing, and maintain audit-ready records.
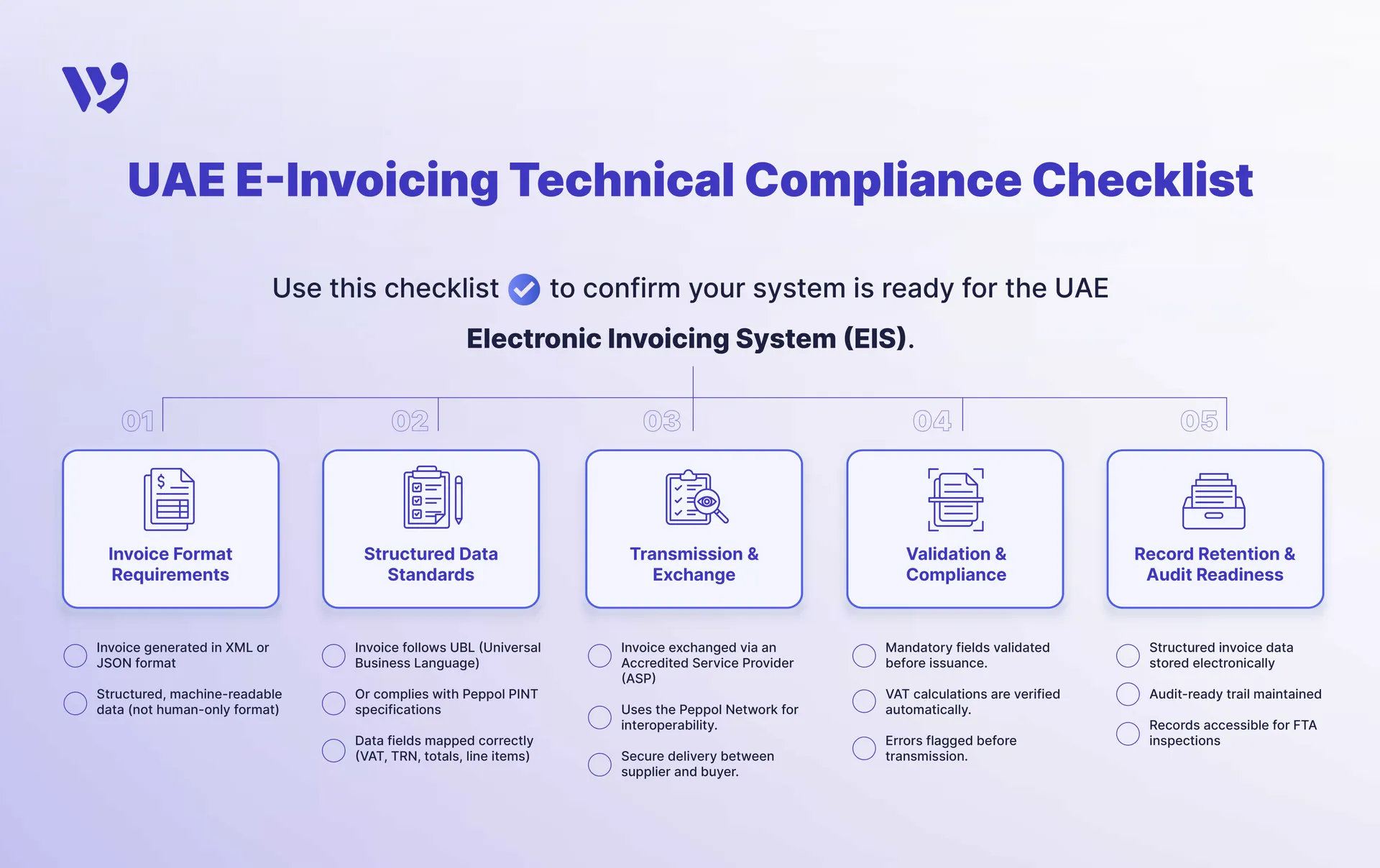
Mandatory Invoice Fields in the UAE
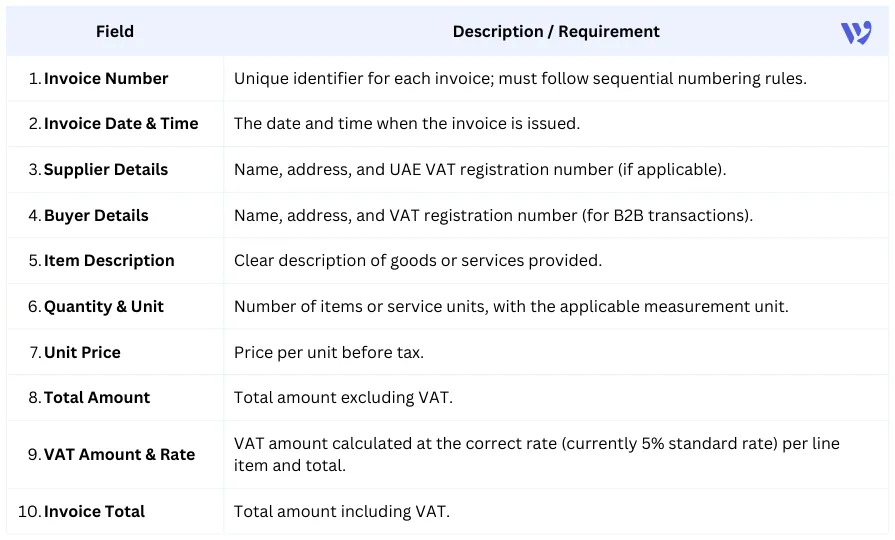
According to the UAE VAT law, all VAT-registered sellers are required to issue a tax invoice for transactions exceeding AED 10,000. These invoices must adhere to specific formats and standards, ensuring readability, authenticity, and compliance with VAT regulations. Mandatory Invoice Fields include:
Compliance is not based on appearance, but on machine-readable, structured data formats.
Compliance is not based on appearance, but on machine-readable, structured data formats.
Mandatory Invoice File Formats
Under the UAE Electronic Invoicing System (EIS), e-invoices must meet strict technical and structural standards. UAE e-invoicing requires invoices to be issued and exchanged in structured electronic formats only:
- XML
- JSON
Required Structured Standards
Invoices must follow internationally recognized structured standards, including:
- UBL (Universal Business Language)
- Peppol PINT (Peppol International Invoice)
These standards ensure:
- Interoperability between suppliers and buyers.
- Consistent data structures across systems.
- Compatibility with Accredited Service Providers (ASPs) and the Peppol network.
Non-Compliant Invoice Formats (Not Accepted)
The following formats do NOT qualify as valid e-invoices under the UAE EIS:
- ❌ PDF invoices (even if emailed)
- ❌ Paper invoices.
- ❌ Scanned documents (JPG, PNG, or image files)
- ❌ Unstructured digital files (Word, Excel, or plain text)
While these formats may still be used for human viewing, they do not meet the legal e-invoicing requirements and cannot replace structured electronic invoices.
Accounting systems that only generate PDFs or manual invoices will not be sufficient once e-invoicing becomes mandatory.
Accounting systems that only generate PDFs or manual invoices will not be sufficient once e-invoicing becomes mandatory.
The Essential Tips for e-Invoicing Compliance
The Essential Tips for e-Invoicing Compliance
- Businesses must generate invoices in XML or JSON format and ensure that their e-invoices remain unaltered from creation to receipt.
- They must apply UBL or Peppol PINT standards and transmit invoices by the Accredited Service Providers.
- Invoices should be readily accessible online, available for download in a readable format such as PDF, and stored as structured invoice data for audit and compliance purposes.
- The use of certified e-signatures is crucial for verifying the authenticity and origin of each invoice.
Preparation Checklist: How to Prepare Before July 2026
With UAE e-invoicing rolling out in phases, businesses should prepare well ahead of their mandatory implementation date. The checklist below outlines practical steps to ensure a smooth and compliant transition.
UAE E-Invoicing Readiness Checklist:
- Identify your implementation phase Confirm whether your business falls under the large businesses, medium enterprises, or SMEs, and note the applicable mandatory deadline.
- Appoint an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) Select and onboard an approved ASP before your phase deadline to enable compliant invoice exchange.
- Upgrade your ERP or accounting system Ensure your system supports structured e-invoices (XML/JSON) and standards such as UBL or Peppol PINT.
- Test e-invoicing workflows in a pilot phase Validate invoice generation, transmission, receipt, and error handling before going live.
- Train finance and operations teams Educate staff on new invoice formats, processes, and compliance responsibilities.
- Implement UAE-based data storage Confirm that invoice data, logs, and audit records are hosted and retained within the UAE.
- Prepare fallback procedures for system outages Define internal processes for incident management, including FTA notification within required timeframes.
Operational Compliance Rules Under UAE E-Invoicing
Beyond technical formats and transmission channels, the UAE Electronic Invoicing System (EIS) imposes operational compliance rules that businesses must follow to remain fully compliant.
These rules govern timing, data storage, system reliability, and audit readiness.
- Invoice Transmission Timeframe All electronic invoices must be issued and transmitted within 14 days of the underlying transaction date. Delays beyond this period may trigger compliance violations and potential penalties once enforcement begins.
- Data Residency Requirement Under UAE e-invoicing regulations, all e-invoice data must be stored within the UAE. This applies to: - Invoice files. - Structured data records. - Audit logs and transaction histories.
- System Failure Reporting Obligations In the event of a system disruption, System failures must be reported to the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) within 2 business days. This applies to both: - Invoice issuers. - Invoice recipients.
Failure to notify the FTA within the prescribed timeframe may result in daily administrative penalties.
Failure to notify the FTA within the prescribed timeframe may result in daily administrative penalties.
- Audit-Ready Storage Responsibilities Both parties involved in an e-invoice transaction are required to:
- Maintain secure, tamper-proof electronic records.
- Ensure invoice data is accessible for audits and inspections.
- Retain structured invoice data in accordance with UAE record-keeping requirements.
Compliance responsibility applies to both the issuer and the recipient, not just the supplier.
Compliance responsibility applies to both the issuer and the recipient, not just the supplier.
UAE E-Invoicing Is Coming — Wafeq Gets You FTA-Ready.
Wafeq is a UAE-built accounting platform designed for modern businesses. With upcoming UAE e-invoicing regulations, Wafeq ensures smooth FTA compliance, accurate VAT reporting, and stress-free invoicing — all from one platform.
Local. Compliant. Built for UAE Businesses.
14,000 +
Companies trust Wafeq for automated invoicing.
4.8/5
Average Rating from Wafeq's customers over the GCC Region.
1st
UAE-Built Peppol Certified Accounting Software.
Why Businesses Trust Wafeq for E-Invoicing?
- Native UAE Accounting System (VAT-ready by default)
- Built for SMEs, startups, and growing companies.
- Arabic & English support.
- Designed to align with FTA workflows and regulations.
How Wafeq Supports Data Compliance
Wafeq provides a full-stack e-invoicing solution designed to meet UAE FTA requirements and scale with your business.
1. FTA-Ready E-Invoicing
Wafeq is built to support UAE e-invoicing requirements through structured invoice generation and Peppol-aligned exchange.
2. Smart Invoice Validation
Automated checks to reduce errors, prevent rejections, and ensure clean invoice submission.
3. Accurate VAT Logic
UAE VAT logic applied at the invoice level for consistent tax calculation and compliance.
4. Automated Reconciliation
Faster matching of invoices with ledger entries, payments, and financial records.
5. Enterprise-Grade Security
Enterprise-grade security with controlled access and compliance-focused data handling.
6. Seamless ERP Integration
Native integration with accounting and ERP workflows for scalable invoicing operations.
As the UAE strives towards a fully digital financial ecosystem, the introduction of obligatory e-invoicing for the B2B sector is a logical progression. These developments not only align with the UAE's digital vision but also set a new standard for business efficiency and compliance.
FAQs about e-Invoicing in the UAE
Is e-invoicing mandatory in the UAE?
Currently, it is not mandatory, but it is expected to become so shortly.
Can you invoice without a VAT number in the UAE?
No, VAT-registered businesses must include their VAT number on invoices.
What are the e-invoicing rules?
The Federal Tax Authority is yet to release comprehensive rules for the implementation of e-invoicing in the UAE.
What is an Accredited Service Provider (ASP)?
An ASP is an MoF-certified intermediary that securely transmits e-invoices between suppliers and buyers via the Peppol network. Businesses must appoint an ASP to ensure compliance with UAE regulations. The requirement to use approved technical channels and service providers is established under the Electronic Invoicing System (EIS) framework defined in Ministerial Decision No. 243 of 2025.
What are the mandatory fields on a UAE e-invoice?
- Invoice number and date.
- Supplier and buyer details (including VAT registration numbers)
- Item description, quantity, and unit price.
- Total amount, VAT rate, and VAT amount.
- Invoice total including VAT.
- Currency and, optionally, payment terms and a unique invoice identifier (UUID)
When do penalties apply?
Penalties are enforced after the mandatory implementation date for each business category, as outlined in Ministerial Decision No. 244 of 2025. Fines can include:
- Monthly fines for system readiness delays.
- Per-invoice or per-credit note fines.
- Daily fines for system failure reporting or data notification lapses.
Can I prepare before my mandatory phase?
Yes. Early adoption is strongly recommended. It allows:
- System testing and error correction.
- Staff training.
- Integration with ASPs.
- Reduced operational disruption once the mandate applies.
Wafeq Accounting Software helps streamline compliance, automate invoicing, and secure your operations ahead of mandatory deadlines. Ensure your business is ready for UAE e-invoicing today.
Wafeq Accounting Software helps streamline compliance, automate invoicing, and secure your operations ahead of mandatory deadlines. Ensure your business is ready for UAE e-invoicing today.




 (1).png?alt=media)
.png?alt=media)

.png?alt=media)
.png?alt=media)





.png?alt=media)
