E-Invoicing in the UAE (2026–2027): What Founders Need to Know

The UAE is set to implement a new e-invoicing regulation in 2026, aimed at digitizing financial transactions, allowing businesses and government real-time visibility over economic activity. This article summarizes a detailed webinar hosted by Nadim Alameddin, CEO of Wafeq, featuring Muhammed Shafeekh, CEO of Finanshels, to provide founders with practical insights on how to prepare for this transformation.
Watch the complete webinar recording on our YouTube channel [includes a demo of Wafeq in action]:
Why E-Invoicing Matters
Shafeekh opened the webinar by explaining the purpose of the regulation:
- E-invoicing is not primarily about tax evasion.
- Governments, like businesses, often operate "blind" without real-time data on transactions, imports, exports, or sector performance.
- Real-time visibility can prevent economic failures, optimize investments, and provide accurate GDP numbers.
- E-invoicing provides the data governments need on transactions as they happen, enabling proactive decision-making.
Understanding E-Invoicing for Business Owners
Many business owners are focused on revenue generation and customer acquisition, often unaware of regulatory changes such as e-invoicing. Shafeekh provided practical guidance:
1. Digital Adoption is Mandatory
- Sales and purchase invoices must be digitally recorded and transmitted to the tax authority.
- Simple PDF invoices or manual systems will not be sufficient.
- A compliant ERP system or accounting software is required to generate XML-format invoices approved by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
2. The Role of Service Providers (ASP)
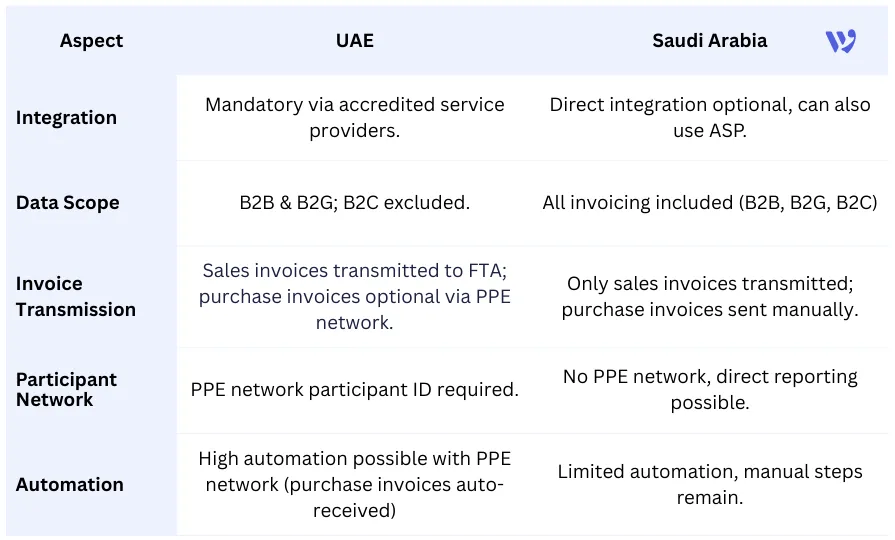
- Businesses can either integrate directly with the tax authority (allowed in Saudi Arabia) or work with an accredited service provider (mandatory in the UAE).
- Approved service providers transmit invoices in compliance with FTA regulations.
3. Who Needs to Comply?
- B2B (Business to Business) and B2G (Business to Government) transactions are included.
- B2C (Business to Consumer) transactions are currently out of scope.
- Turnover thresholds:
- Above AED 50 million: pilot begins July 31, 2026; mandatory from January 1, 2027. - Below AED 50 million: pilot begins March 31, 2027; mandatory from July 1, 2027.
Preparing Your Business for E-Invoicing
Shafeekh highlighted key preparation steps for SMEs and larger enterprises:
1. ERP & Accounting Software
- Use an ERP or accounting system compliant with FTA standards.
- Ensure the system can generate XML invoices in the UBL standard format, with local UAE extensions as VAT, place of supply, and free zone details.
2. Customer & Master Data
- Validate customer information: full address, and VAT/TRN numbers.
- Correct classification of invoices (zero-rated, exempt, standard-rated, free zone, non-free zone).
3. Workflows & Processes
- Define approval, rejection, refund, and discount processes.
- Map all edge cases to ensure smooth day-to-day operations.
- Pilot testing is recommended to identify and resolve issues early.
4. Voluntary Adoption Phase
- Encouraged all businesses to adopt early, allowing adjustments without penalties.
- Errors during voluntary adoption will not result in fines, providing an opportunity to adapt workflows.
Key Differences Between UAE and Saudi E-Invoicing
Shafeekh and Nadim compared practices in both countries:
Important Dates for UAE Businesses
- Pilot phase for companies >50 million AED turnover: 31 July 2026.
- Mandatory adoption: 1 January 2027.
- SMBs (<50 million AED): Pilot starts 31 March 2027, mandatory 1 July 2027.
- Voluntary adoption is recommended to prepare systems and workflows without risk.
Practical Day-to-Day Changes
Once e-invoicing goes live, Shafeekh explained:
- Invoices are permanently frozen after reporting.
- Errors are corrected through credit notes and issuing new invoices.
- Workflow discipline is essential for approvals, rejections, and compliance.
- Data cleaning is critical; incorrect customer or invoice data may result in reporting delays.
Key Learnings from Saudi Implementation
Key Learnings from Saudi Implementation
Nadim added lessons from Saudi Arabia:
- Invoice data accuracy is vital. Missing TRNs or addresses can prevent reporting.
- B2B invoices with missing details were sometimes reported as B2C simplified invoices.
- Tax authorities initially exercise leniency, providing warnings before fines.
Longer-Term Implications
1. VAT Returns
- E-invoicing simplifies VAT returns, but manual checks and tax expertise remain necessary.
- B2C transactions and cross-border invoices still require separate reporting.
2. Audit Readiness
- Digitized, standardized invoices improve audit accuracy.
- Revenue recognition and categorization processes may require revision.
- Accounting workload is reduced for manual entry, freeing time for strategic work.
3. Cross-Border Transactions
- Suppliers using e-invoicing in other countries (e.g., France) can send XML invoices in a compatible UBL format.
- Facilitates global trade and integration with the UAE PPE network.
Action Plan for Founders
Action Plan for Founders
Shafeekh and Nadim recommended:
- Ensure your ERP/accounting software supports e-invoicing.
- Choose an accredited service provider if required.
- Clean and validate master data (customers, products, tax details).
- Define workflows for approvals, rejections, discounts, and credit notes.
- Participate in the voluntary adoption phase to test systems before mandatory deadlines.
- Begin planning at least 3–6 months before the go-live date.
Audience Q&A
During the webinar, several practical questions were raised by attendees. Nadim and Shafeekh provided detailed answers to help businesses prepare for the UAE e-invoicing.
Q1: What happens if we make a mistake in an invoice after the reporting?
- Once an invoice is reported, it cannot be edited.
- Any errors must be corrected using a credit note and a new invoice.
- Workflow discipline is essential to prevent repeated errors.
Q2: Are B2C invoices included in e-invoicing?
Currently, e-invoicing in the UAE applies only to B2B and B2G transactions. B2C invoices are out of scope, but businesses should still maintain accurate records for VAT reporting.
Q3: Can we adopt e-invoicing voluntarily before the mandatory deadline?
Yes, voluntary adoption is encouraged. This allows businesses to test their systems, workflows, and data accuracy without facing penalties.
Q4: How do we handle cross-border invoices?
Suppliers using international systems can send invoices in UBL/XML format that comply with the UAE PPE network. This facilitates automation and integration even for international transactions.
Q5: What are the consequences of missing customer data?
Missing TRNs, addresses, or invoice details can prevent reporting. During voluntary adoption, errors are flagged as warnings, allowing correction before mandatory deadlines.
Q6: Do we need to upgrade our ERP system to comply?
Yes, your ERP or accounting system must generate FTA-compliant invoices in XML format with the required UAE extensions. Using an accredited service provider is mandatory for connecting with the PPE network.
Q7: How does e-invoicing affect VAT returns?
Automation reduces manual entry, simplifies VAT returns, and ensures accurate categorization. B2C transactions and non-standard cases still require separate attention.
Ready for UAE E-Invoicing?
Ready for UAE E-Invoicing?
Simplify compliance, automate your invoicing, and stay ahead with Wafeq Accounting Software, your all-in-one accounting solution and accredited service provider.




 (1).png?alt=media)
.png?alt=media)

.png?alt=media)
.png?alt=media)





.png?alt=media)
